321 Stainless for High Temperature Applications
- HOME
- Tig Welding Stainless
- Tig Welding Stainless Steel
- 321 Stainless
When Is 321 Stainless Preferred Over 304L or 316L Stainless?
Importance of Choosing the Right Stainless Steel Grade
In industries where materials are pushed to their limits—through extreme heat, pressure, or chemical exposure—choosing the correct stainless steel grade is absolutely critical. It’s not just about corrosion resistance or strength anymore; thermal stability, weldability, and long-term durability all come into play. Among the commonly used grades, 304L is often the go-to. But in specific high-temperature environments,
321 stainless steel becomes the preferred option.
If you are still using the standard TIG cups and hardware that came with your machine or TIG torch, I can just about guarantee you will get better results if you upgrade to a weldmonger® stubby gas lens kit.
304L vs 321: Why the Comparison Matters
304L is well-known for its corrosion resistance, ease of fabrication, and affordability. But it has a major weakness when exposed to high temperatures for extended periods—sensitization.
That’s where 321 comes in.
Designed to combat the issues 304L can’t handle, 321 stainless is tailor-made for elevated temperature service, making it a valuable alternative in industrial settings.
Understanding 321 Stainless Steel
Role of Titanium in 321 Stainless
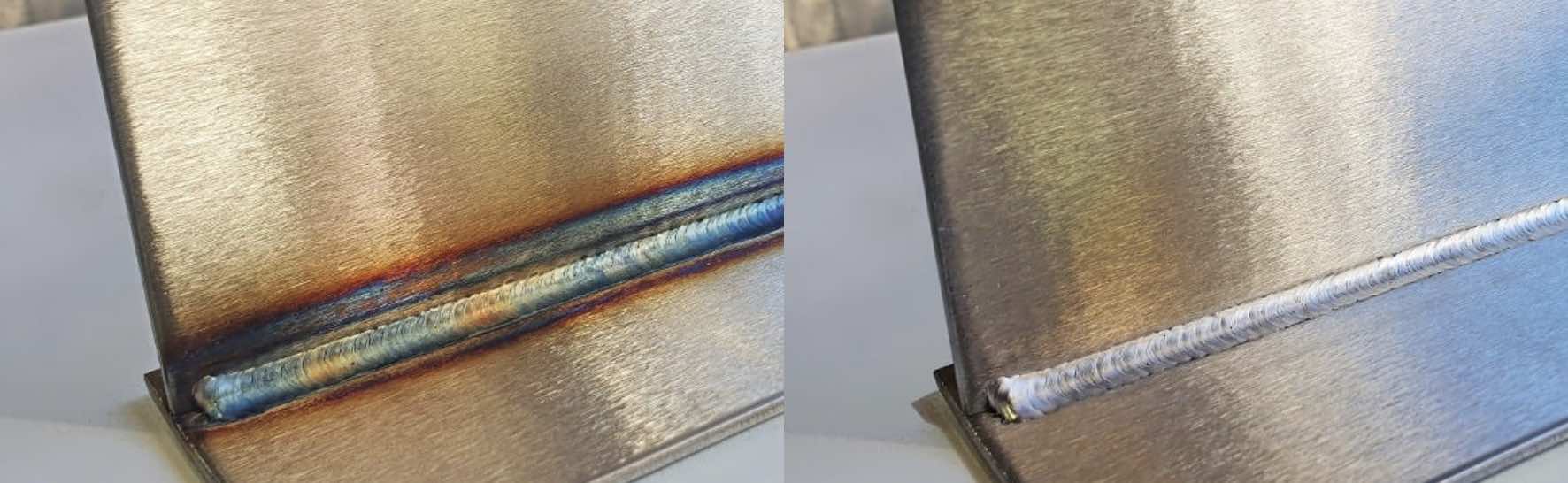
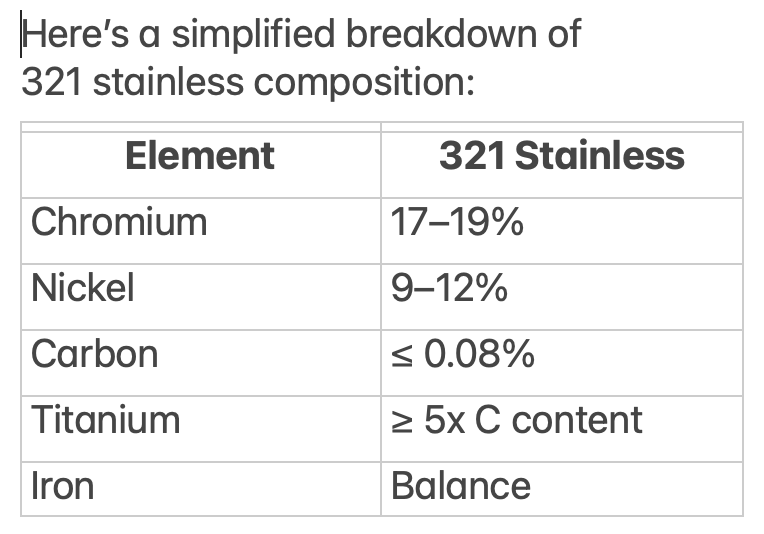
Titanium binds with carbon to form titanium carbides, which prevents chromium carbide precipitation during welding and high-temperature exposure. This stabilization eliminates the risk of intergranular corrosion—a problem 304L can face when exposed to temperatures between 800°F and 1500°F.
Differences Between 304L and 321 Stainless Steel
While both are austenitic and contain similar levels of chromium and nickel, 321’s inclusion of titanium gives it the edge in high-heat applications. 304L lowers carbon to prevent carbide precipitation, but under prolonged high temperatures, 304L still risks losing corrosion resistance.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Stability
Here’s the big one: 321 outperforms 304L in temperatures above 900°F (480°C).
It retains its mechanical strength and resists scaling and oxidation much better. This makes 321 a solid choice for continuous or repeated heat exposure.
Weldability and Corrosion Resistance
Both grades are easy to weld, but 321 stainless holds its corrosion resistance even in the heat-affected zones (HAZ), whereas 304L might suffer from sensitization without additional heat treatment.
When to use 321 Stainless Over 304L
High Temperature Applications
If equipment or components will be regularly exposed to high heat, 321 is the smarter pick. It withstands sustained heat better than 304L without becoming brittle or losing its structural integrity.
321 stainless steel is widely for automotive, motorsports, and aircraft exhaust components.
Examples where 321 stainless steel is used:

Aerospace Industry
Jet Engine Components
One of the most high-stress environments known to man is inside a jet engine. Components in this setting are constantly exposed to rapid thermal cycling, intense vibration, and high-temperature gases.
Aircraft Exhaust Systems
321 stainless is preferred for aircraft exhaust stacks and manifolds because of its thermal fatigue resistance. Unlike 304L, it doesn’t become brittle after multiple heating and cooling cycles, ensuring long-term reliability in flight.
Heat Shields and Ducting
321’s combination of formability and thermal resistance makes it perfect for ducts and shielding that protect aircraft components from engine heat.
Automotive Sector
Turbocharger Systems
Turbochargers are small but mighty devices that face intense exhaust gas temperatures. 321 stainless is used in the hot side of turbochargers, where temperatures can exceed 1000°F. Its resistance to scaling and cracking makes it ideal for performance and endurance vehicles.
High-Performance Exhaust Manifolds
Street and race cars with upgraded exhaust systems often feature 321 stainless manifolds. These parts can handle higher thermal loads without warping or failing, making them a favorite for custom builders and motorsports teams.
Heat Treatment and Thermal Processing
Furnace Parts
In industrial furnaces, components like trays, muffles, and baskets are subjected to extreme temperatures. 321 stainless holds up where lesser grades warp or crack, making it a long-lasting option in heat treatment shops.
Equipment that operates at sustained high temperatures—such as annealing enclosures or radiant heating tubes—often uses 321 to ensure consistent performance over long production cycles.
Chemical and Petrochemical Plants
High-Temperature Heat Exchangers
When dealing with high-pressure and corrosive heat transfer fluids, 321 stainless is a smart choice. Its strength at elevated temperatures and resistance to oxidation make it suitable for demanding chemical environments.
Chemical Reactors and Piping
321 is used in reactor vessels and high-temperature piping systems that transport acids, alkalis, or solvents under pressure. Its performance reduces the risk of premature corrosion or material failure.
Oil and Gas Industry
Refinery Equipment
Refineries expose materials to intense heat, pressure, and reactive chemicals. 321 is commonly used in:
- Furnace liners
- Flue gas systems
- Reformer tubes
Its thermal and structural stability give it an edge over standard stainless steel.
Heat-Resistant Tubing and Valves
Oil and gas pipelines often include sections exposed to flare stacks or combustion areas. 321 stainless tubing and valves maintain integrity, preventing leaks or system failures.
Power Generation
Steam Superheaters
321 stainless is a standard material in steam superheater coils within fossil-fuel power plants. It resists oxidation and creep deformation at high temperatures.
Boiler Tubes and Headers
In high-pressure boilers, where stress and heat are unrelenting, 321 stainless proves its worth. It maintains pressure tolerance and doesn't scale or degrade as quickly as standard steel.
Food and Beverage Processing
Equipment Exposed to High-Temperature Sanitization
Food processing often involves steam cleaning and pasteurization, which can degrade certain materials. 321 stainless holds up to repeated sterilization without losing strength or corroding.
Conveyor Systems Near Heat Sources
In baking and thermal processing lines, conveyors must endure constant heat. 321’s thermal fatigue resistance makes it a smart material for moving parts near ovens and burners.
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
Sterilization Equipment
Autoclaves, steam chambers, and sterile mixing tanks rely on 321 stainless for its high-temperature resistance and cleanability.
Heated Mixing and Storage Vessels
Where medicines or chemicals are heated and mixed under sterile conditions, 321 maintains its shape, cleanliness, and resistance to degradation.
Other Niche Applications
Expansion Joints
321 stainless is used in metal bellows and expansion joints, which must absorb movement while withstanding high temperatures. These are found in both industrial and aerospace systems.
Bellows and Flexible Metal Hoses
Flexible connectors that handle hot air or fluids often use 321 to avoid cracking and fatigue from temperature cycling.
Conclusion
321 stainless steel shines in the heat—literally and figuratively. It’s not just a substitute for 304L; it’s a high-performance solution for industries that demand superior thermal stability, weld integrity, and corrosion resistance at high temperatures. From jet engines to autoclaves, 321 is a trusted material when failure simply isn’t an option.
FAQs
1. Why is 321 stainless better than 304 in heat applications?
Because it’s stabilized with titanium, 321 resists carbide precipitation and intergranular corrosion at elevated temperatures, unlike 304.
2. Can 321 be used in food-grade applications?
Yes. It meets food safety standards and is ideal where frequent high-heat cleaning is required.
3. Is 321 suitable for marine environments?
No. It lacks molybdenum and doesn’t resist chlorides well. For marine use, 316L is the better option.
4. How does titanium affect 321 stainless steel performance?
Titanium binds with carbon, preventing chromium carbide formation during welding or heat exposure. This maintains corrosion resistance.
5. Is 321 magnetic after fabrication?
It is generally non-magnetic in its annealed state but may show slight magnetism after cold working.